Inflammatory Bowel Disease
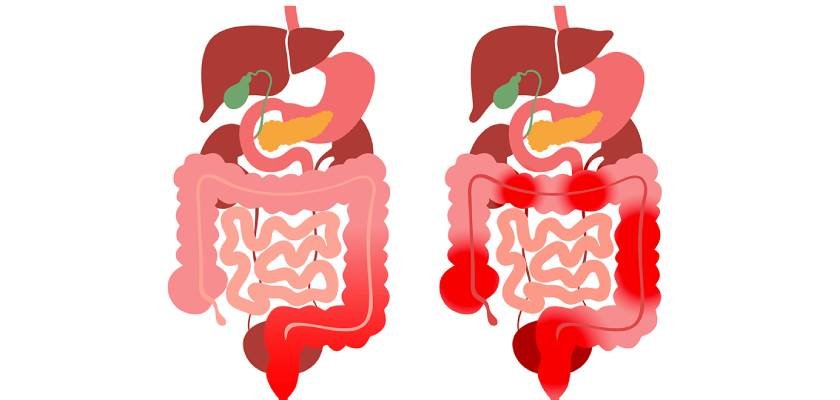
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) is a term used to describe chronic inflammatory conditions of the gastrointestinal tract, primarily including Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. These conditions cause inflammation and damage to the digestive tract, leading to a range of symptoms and complications. IBD can significantly impact quality of life, causing persistent abdominal pain, diarrhea, weight loss, and fatigue. The exact cause of IBD is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors. Effective management often involves a combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and sometimes surgery, aimed at controlling inflammation and improving overall health.
Key Features of Inflammatory Bowel Disease:
Types:
- Crohn's Disease: Can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract from the mouth to the anus, characterized by transmural inflammation (inflammation that affects the entire thickness of the bowel wall).
- Ulcerative Colitis: Primarily affects the colon and rectum, causing inflammation and ulcers on the inner lining of the large intestine.
Common Symptoms:
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Persistent diarrhea, which may be bloody or contain mucus
- Weight loss and loss of appetite
- Fatigue and general malaise
- Urgency to have bowel movements
- Fever and night sweats
Diagnosis:
- Medical History and Physical Exam: Assessment of symptoms, family history, and physical examination.
- Laboratory Tests: Blood tests to check for anemia, inflammation markers, and electrolyte imbalances.
- Stool Tests: To rule out infections and assess for the presence of blood or inflammation.
- Imaging Studies: CT scans, MRI, or ultrasound to visualize the extent of inflammation and detect complications.
- Endoscopy: Colonoscopy or upper endoscopy to directly examine the gastrointestinal tract and obtain biopsy samples.
Management and Treatment:
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory drugs (e.g., corticosteroids), immunosuppressants, and biologics to control inflammation and manage symptoms.
- Dietary Adjustments: Tailored diets to avoid trigger foods and ensure proper nutrition.
- Lifestyle Changes: Stress management, regular exercise, and smoking cessation.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove damaged sections of the bowel or address complications.
- Regular Monitoring: Ongoing assessment to monitor disease activity, treatment efficacy, and manage potential complications.
When to Seek Medical Help:
- Persistent or worsening symptoms despite treatment
- Severe abdominal pain, significant weight loss, or fever
- Signs of complications, such as rectal bleeding, obstruction, or fistulas
- New or unusual symptoms that impact daily life
Inflammatory Bowel Disease requires comprehensive management to control inflammation, alleviate symptoms, and prevent complications. If you or a loved one are experiencing symptoms of IBD, it is important to seek medical care for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. Our hospital provides specialized care for IBD, focusing on effective management and support to improve quality of life. Contact us to schedule an appointment with our expert team in gastroenterology.
Emergency Cases
Please feel welcome to contact our friendly reception staff with any general or medical enquiry call us.
